 |
|||
| HSG |
|
Rechnen im 100 000er-System
1.234.567.890 · 7.835.007.219 = ?
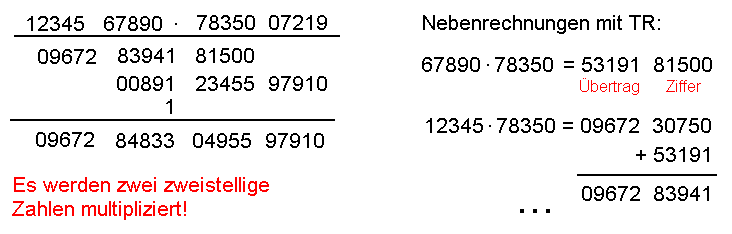
Aufgabe
Berechne im 100 000er-System 479.001.600 · 5.079.110.400 ganz exakt. Das Ergebnis ist übrigens 20! .
Langzahlarithmetik mit GInt
Ausschnitte aus der Schnittstelle
Type
TCompare = (Lt, St, Eq, Er);
TSign = (negative, positive);
TFGInt = Record
Sign : TSign;
Number : Array Of LongWord;
End;
....
// Compare 2 FGInts in absolute value, returns
// Lt if FGInt1 > FGInt2, St if FGInt1 < FGInt2, Eq if FGInt1 = FGInt2,
// Er otherwise
Function FGIntCompareAbs(Const FGInt1, FGInt2 : TFGInt) : TCompare;
....
// Convert a base 10 string to a FGInt
Procedure Base10StringToFGInt(Base10 : String; Var FGInt : TFGInt);
....
// Convert a FGInt to a base 10 string
Procedure FGIntToBase10String(Const FGInt : TFGInt; Var Base10 : String);
....
// Add 2 FGInts, FGInt1 + FGInt2 = Sum
Procedure FGIntAdd(Const FGInt1, FGInt2 : TFGInt; Var Sum : TFGInt);
Delphi-Hilfe: Longword, 0..4 294 967 295, 32 Bit, ohne Vorzeichen
GInt speichert in Number[0] die Anzahl der 'Ziffern'. Jede 'Ziffer' hat nach der String-zu-TFGInt-Umwandlung zunächst 4 Dezimalstellen. Damit ist sichergestellt, dass das 'kleine Computer-Einmaleins' reicht, um zwei 'Ziffern' miteinander zu multiplizieren. Für 5-stellige 'Ziffern' reicht der Wertebereich leider nicht, denn 99999·99999 = 9 999 800 001 > 4 294 967 295. Hier kann ein 10-stelliger Taschenrechner mehr!
